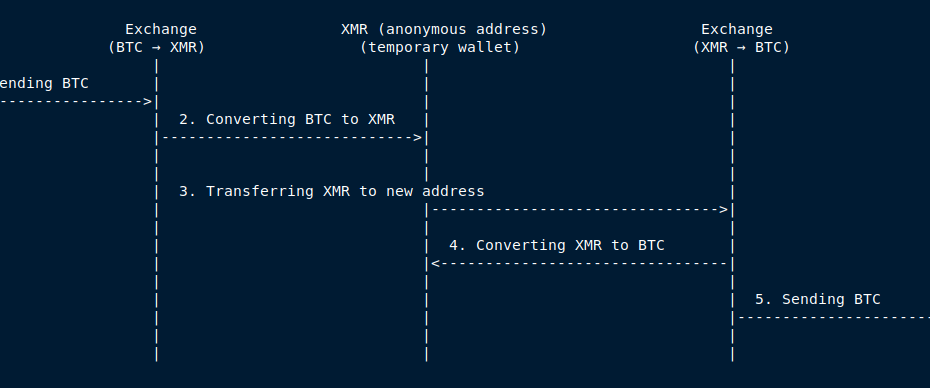
A scheme to break the link between two BTC addresses using the anonymous cryptocurrency Monero (XMR) can be described as follows:
Suppose John wants to receive clean anonymous BTC from his (possibly tainted) BTC. For this, he will need two BTC wallets and two XMR wallets. Naturally, it’s essential to consider anonymity aspects on the Internet, such as using the Tor network, possibly Tor + VPN, or other proxy services.
Here’s what we’ll need:
- BTC Wallet 1 with tainted BTC
- New XMR Wallet 1
- New anonymous XMR Wallet 2
- New anonymous BTC Wallet 2 for clean BTC
Step 1: Sending BTC to the Exchange
- Sender John (BTC address BTC1) sends Bitcoin (BTC) to a cryptocurrency exchange that supports anonymous exchanges (e.g., using atomic swaps or specialized services).
- The exchange receives BTC and initiates the exchange to Monero (XMR).
Step 2: Exchanging BTC to XMR
- The exchange converts the received BTC to XMR, using internal reserves or a trading mechanism.
- As a result of this exchange, XMR is credited to a temporary anonymous XMR1 wallet belonging to John.
Step 3: Transferring XMR to a New Address XMR-2 (created anonymously)
- From the temporary XMR-1 wallet belonging to the sender, XMR is transferred to a new anonymous XMR2 address, which belongs to the recipient or an intermediary.
- This step adds an additional level of anonymity, as Monero transactions inherently conceal transaction details, making the link between inputs and outputs nearly impossible to trace.
Step 4: Exchanging XMR back to BTC
- John or intermediary, having XMR in their anonymous XMR-2 wallet, sends XMR to another exchange (or the same one, though it’s not recommended for increased anonymity).
- The exchange converts the received XMR back to BTC.
Step 5: Sending BTC to the Final Address
- The exchange sends the received BTC to the final BTC-2 address.
- John (address BTC-2) receives BTC, completing the transaction chain.
Final Scheme:
- BTC (address BTC-1) → Exchange (BTC → XMR) → XMR-1 (anonymous address) → XMR-2(new anonymous address XMR-2) → Exchange (XMR → BTC) → BTC (address BTC-2).
Thus, the link between BTC-1 and BTC-2 addresses is broken using anonymous Monero transactions, making it nearly impossible to trace the original and final addresses in the Bitcoin network.
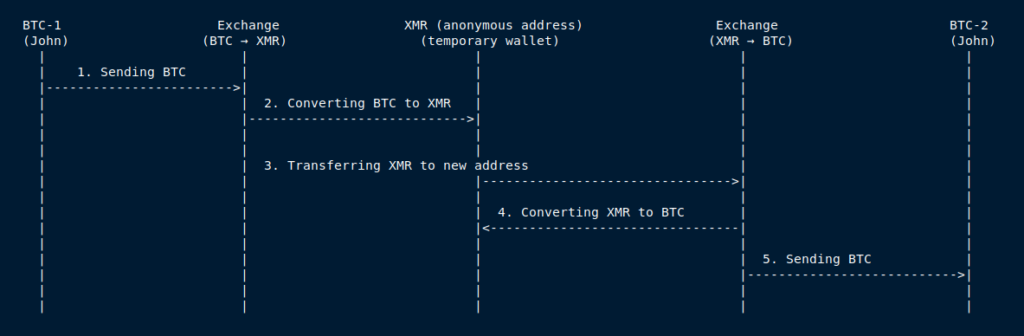
Diagram
- Sending BTC: The sender transfers BTC from address BTC-1 to the exchange
- Converting BTC to XMR: The exchange converts the received BTC to XMR and credits it to a temporary anonymous XMR-1 address
- Transferring XMR to a new address: XMR is transferred to a new address XMR-2, belonging to the recipient
- Converting XMR to BTC: The recipient or intermediary sends XMR to an exchange, which converts it back to BTC
- Sending BTC: The exchange transfers the received BTC to the final address BTC-2